Unearthing the Academic Time Capsule: Delving into the Evolution of Science Education Among Indonesian Students
Abstract
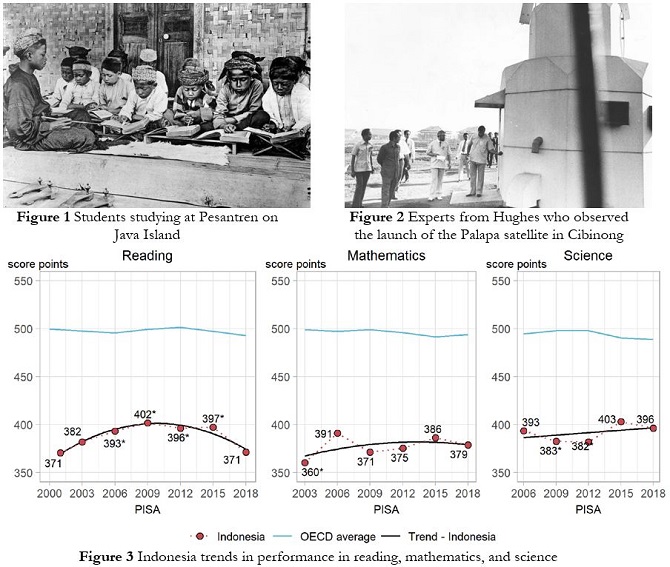
The Indonesian education system, in general, still has many challenges in learning science. The results of the 2018 PISA survey put Indonesia in 74th place, which is sixth from the bottom. Indonesian students' reading ability, with a score of 371, is in the 74th position; Mathematics, with 379, is in the 73rd position; and Science, with a score of 396, is in the 71st position. This situation is intriguing to explore how history influences the education system's current conditions, especially in science learning. The article will explore the effect of changes in the education system on science learning in Indonesia. Exploration of science learning will start from the education system before the independence of Indonesia to the current education system. Using a historical approach, and this article concludes that political power influences change in the ideological orientation of the system and the direction of education, especially in education policy, curriculum changes, and learning activities. This change in situation plays a huge role in determining the achievements of current science learning and achievements.
Full Text:
Download PDFReferences
Adha, M. A., Gordisona, S., Ulfatin, N., & Supriyanto, A. (2019). Analisis Komparasi Sistem Pendidikan Indonesia dan Finlandia [Comparative Analysis of Indonesian and Finnish Education Systems]. Tadbir : Jurnal Studi Manajemen Pendidikan, 3(2), 145–160. https://doi.org/10.29240/jsmp.v3i2.1102
Akiba, M., Chiu, Y. L., Shimizu, K., & Liang, G. (2012). Teacher salary and national achievement: A cross-national analysis of 30 countries. International Journal of Educational Research, 53, 171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2012.03.007
Bjork, C. (2005). Indonesian education: Teachers, schools, and central bureaucracy. Routledge.
Budiarti, Y. (2018). Pendidikan Dan Pembelajaran Berdasarkan Dari Sudut Pandang Histori [Education and Learning Based From a Historical Perspective]. Jurnal Majalah Kreasi STKIP MPL, 10(2), 18–31.
Budiman, A., Roan, A., & Callan, V. J. (2013). Rationalizing Ideologies, Social Identities and Corruption Among Civil Servants in Indonesia During the Suharto Era. Journal of Business Ethics, 116(1), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-012-1451-y
Darling-Hammond, L. (2000). Teacher quality and student achievement. A review of state policy evidence. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 8(1), 1–44.
Darling-Hammond, L., & Lieberman, A. (2013). Teacher education around the world. Routledge.
Darling-Hammond, L., Newton, X., & Wei, R. C. (2010). Evaluating teacher education outcomes: A study of the Stanford teacher education program. Journal of Education for Teaching, 36(4), 369–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/02607476.2010.513844
Dharmaningtias, D. S. (2013). Penghapusan Kebijakan Rintisan Sekolah Berstandar Internasional (RSBI) [Elimination of the International Standard School Pilot Policy (RSBI)]. Jurnal Politica Dinamika Masalah Politik Dalam Negeri Dan Hubungan Internasional, 4(2), 263–285.
Ding, C., & Sherman, H. (2006). Teaching Effectiveness and Student Achievement: Examining the Relationship. Educational Research Quarterly, 29(04), 40–51.
Djojonegoro, W. (1997). Fifty years of Indonesian education development. Jakarta: Depdikbud.
Emmerson, D. K. (1999). Indonesia Beyond Suharto. In Indonesia Beyond Suharto: Polity, economy, society, transition. Routledge.
Emmerson, D. K. (2021). 4. The Bureaucracy in Political Context: Weakness in Strength. In Political Power and Communications in Indonesia (pp. 82–136). University of California Press Berkeley.
Fendler, J., & Gläser-Zikuda, M. (2013). Teaching experience and the "Shift from teaching to learning". Zeitschrift Für Hochschulentwicklung, 8(3), 15–28.
Gerritsen, S., Plug, E., & Webbink, D. (2017). Teacher Quality and Student Achievement: Evidence from a Sample of Dutch Twins. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 32(3), 643–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.2539
Gershenson, S. (2016). Linking teacher quality, student attendance, and student achievement. Education Finance and Policy, 11(2), 125–149. https://doi.org/10.1162/EDFP_a_00180
Goss, A. (2009). Decent colonialism? Pure science and colonial ideology in the Netherlands East Indies, 1910–1929. Journal of Southeast Asian Studies, 40(1), 187–214.
Guinness, P. (1989). Social harmony is ideology and practice in a Javanese city. Creating Indonesian Cultures, 3, 55–74.
Gutierrez, A., Fox, J. L., Alexander, C., Colette, A., & Alexander, C. (2019). Professionalism and teacher education : voices from policy and practice. Springer.
Hamidah, H., Junaedi, I., Mulyono, M., & Kusuma, J. W. (2021). Kurikulum dan Pembelajaran Matematika di Jepang dan di Indonesia [Mathematics Curriculum and Learning in Japan and in Indonesia]. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika (JPM), 7(2), 95–105.
Harris, D. N., & Sass, T. R. (2011). Teacher training, teacher quality, and student achievement. Journal of Public Economics, 95(7–8), 798–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2010.11.009
Hicks, D., & Peacock, J. L. (1973). Indonesia: An Anthropological Perspective. Goodyear Publishing Company.
Hoesny, M. U., & Darmayanti, R. (2021). Permasalahan dan Solusi Untuk Meningkatkan Kompetensi dan Kualitas Guru: Sebuah Kajian Pustaka [Problems and Solutions to Improve Teacher Competence and Quality: A Literature Review]. Scholaria: Jurnal Pendidikan Dan Kebudayaan, 11(2), 123–132.
Istanti, D. J. (2019). Dinamika Kebijakan Kurikulum Pendidikan di Indonesia Pasca Reformasi [Dynamics of Education Curriculum Policy in Post-Reform Indonesia]. Jurnal Ilmu Politik Dan Pemerintahan, 5(2), 140–156.
Koentjaraningrat. (1975). Introduction to the Peoples and Cultures of Indonesia and Malaysia. Menlo Park, Calif.: Cummings Publishing Company.
Lavi, R., Tal, M., & Dori, Y. J. (2021). Perceptions of STEM alumni and students on developing 21st century skills through methods of teaching and learning. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 70, 101002.
Maulipaksi, D. (2016). 7 Provinsi Raih Nilai Terbaik Uji Kompetensi Guru 2015 [7 Provinces Get the Best Scores in 2015 Teacher Competency Test]. Kementerian Pendidikan Dan Kebudayaan. https://www.kemdikbud.go.id/main/blog/2016/01/7-provinsi-raih-nilai-terbaik-uji-kompetensi-guru-2015
McLeod, R. (2000). Soeharto’s Indonesia: A Better Class of Corruption. Agenda - A Journal of Policy Analysis and Reform, 7(2), 99–112. https://doi.org/10.22459/ag.07.02.2000.01
Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology. (2020). Program Organisasi Penggerak [Driving Organization Program]. https://sekolah.penggerak.kemdikbud.go.id/organisasipenggerak
Muharani, A., & Hudaidah, H. (2021). Dampak Masuknya Hindu Budha Terhadap Pendidikan di Indonesia [The Impact of Hindu-Buddhist Entry on Education in Indonesia]. Edukatif: Jurnal Ilmu Pendidikan, 3(3), 928–934.
Mukodi. (2016). Refleksi Dinamika Kebijakan Pendidikan di Indonesia [Reflection on the Dynamics of Education Policy in Indonesia]. Jurnal Profesi Pendidik, 3(2), 141–152.
OECD. (2018). Indonesia Student performance (PISA 2018). https://gpseducation.oecd.org/CountryProfile?primaryCountry=IDN&treshold=10&topic=PI#:~:text=In reading literacy%2C the main,487 points in OECD countries.
Oktaviyanti, D., Kusbiantono, K., Sari, K., M.Arifin, Rahayu, S., & Asmara, A. Y. (2014). Analisis Perkembangan Kebijakan Ilmu Pengetahuan dan Teknologi di Indonesia dari Era Orde Lama hingga Era Orde Baru [Analysis of the Development of Science and Technology Policy in Indonesia from the Old Order Era to the New Order Era]. Lembaga Ilmu Pengetahuan Indonesia. http://lipi.go.id/publikasi/1analisis-perkembangan-kebijakan-ilmu-pengetahuan-dan-teknologi-di-indonesia-dari-era-orde-lama-hingga-era-orde-baru-/16386
Park, W., Wu, J. Y., & Erduran, S. (2020). The Nature of STEM Disciplines in the Science Education Standards Documents from the USA, Korea and Taiwan: Focusing on Disciplinary Aims, Values and Practices. Science and Education, 29(4), 899–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11191-020-00139-1
Postlethwaite, T. N., & Thomas, R. M. (1980). Schooling in the ASEAN region: Primary and secondary education in Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand (1st ed.). Elsevier.
Pramana, C., Chamidah, D., Suyatno, S., Renadi, F., & Syaharuddin, S. (2021). Strategies to Improved Education Quality in Indonesia: A Review. Turkish Online Journal of Qualitative Inquiry, 12(3), 1977-1994.
Quive, L. G., Leandro, S., Bandali, E. C., Gueze, G. A., João, D. A., Gomundanhe, A. M., Neuana, N. F., & Macuvele, D. L. P. (2021). Exploring materials locally available to teach chemistry experimentally in developing countries. Education for Chemical Engineers, 34, 1–8.
Ramli, M. (2010). Primary School System in Java Before and Under Japanese Occupation (1940-1944). Historia: Jurnal Pendidik Dan Peneliti Sejarah, 11(1), 66–83.
Ricklefs, M. C. (1991). A History of Modern Indonesia since c. 1300. The Macmillan Press Ltd.
Rockoff, J. E. . (2004). The Impact of Individual Teachers on Student Achievement : Evidence from Panel Data Source. The American Economic Review, 94(2), 247–252.
Safei, H., & Hudaidah, H. (2020). Sistem Pendidikan Umum Pada Masa Orde Baru (1968-1998)[General Education System During the New Order Period (1968-1998)]. Jurnal Humanitas, 7(1), 1–13.
Setiawan, B., & Suwandi, E. (2022). The Development of Indonesia National Curriculum and Its Changes: The Integrated Science Curriculum Development in Indonesia. Journal of Innovation in Educational and Cultural Research, 3(4), 528–535.
Stenmark, M. (2005). A religiously partisan science? Islamic and Christian perspectives. Theology and Science, 3(1), 23–38.
Subkhan, E. (2018). Ideologi, Kekuasaan, Dan Pengaruhnya Pada Arah Sistem Pendidikan Nasional Indonesia (1950-1965) [Ideology, Power, and Their Influence on the Direction of the Indonesian National Education System (1950-1965)]. Journal of Indonesian History, 7(1), 19–34.
Suharno, Pambudi, N. A., & Harjanto, B. (2020). Vocational education in Indonesia: History, development, opportunities, and challenges. Children and Youth Services Review, 115, 105092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105092
Suratno, T. (2014). The education system in Indonesia at a time of significant changes. Revue Internationale d’éducation de Sèvres.
Syaharuddin, S., & Susanto, H. (2019). Sejarah Pendidikan Indonesia (Era Pra Kolonialisme Nusantara sampai Reformasi) [History of Indonesian Education (Pre-Colonial Archipelago Era to Reformation)]. FKIP Universitas Lambung Mangkurat.
Timmons, G. (1996). Science and education in the first half of the nineteenth century. Endeavour, 20(4), 140–143.
Tinker, T. (2004). The Enlightenment and its discontents: Antinomies of Christianity, Islam and the calculative sciences. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 17(3), 442–475.
Turner, R., Camilli, G., Kroc, R., & Hoover, J. (1986). Policy Strategies, Teacher Salary Incentive, and Student Achievement: An Explanatory Model. Educational Researcher, 15(3), 5–11. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X015003005
Tytler, R., & Osborne, J. (2012). Student attitudes and aspirations towards science. In Second International Handbook of Science Education (pp. 597–625). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-9041-7_41
Watson, C. W., & Kipp, R. S. (1995). Dissociated Identities: Ethnicity, Religion, and Class in an Indonesian Society. The Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute, 1(2), 444. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3034739?origin=crossref
White, E. (2014). Being a teacher and a teacher educator - developing a new identity? Professional Development in Education, 40(3), 436–449. https://doi.org/10.1080/19415257.2013.782062
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17509/jsl.v6i4.60828
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2023 Ikmanda Nugraha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi 229 Bandung 40154, West Java, Indonesia










